Reproductive Anatomy
From: http://www2.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/biobookreprod.html
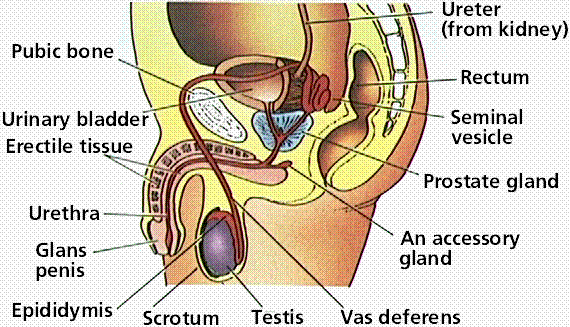
Male Reproductive System:
-
Testes- Commonly known as the testicles, they are responsible from for the production of sperm cells and testosterone.
-
Epididymis- A mass of tubes that carries sperm from the testes to the vas deferens. It matures as it goes through this process so that by the time it reaches the vas deferens, the sperm is ready to fertilize an egg.
-
Penis- The external sex organ. It contains the urethra which is used for urination and to deliver semen.
-
Prostate- This gland is found only in males and helps with production and ejaculation of semen.
-
Seminal Vesicle- Small sacs in which seminal fluid is stored
-
Urethra- This is a tube that carried urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
-
Urinary Bladder-A hollow organ that functions as the body’s urine storage unit. Urine comes from the kidneys through the ureters and leaves through the urethra.
(Taylor, n.d.)
(From: http://web.carteret.edu/keoughp/LFreshwater/NEO/blackboard/EmbDev/female_reproductive_organs.htm)
Female Reproductive System:
-
Breasts- Each female has two of these milk-producing glands. They are made up of the areola, the nipple, and the mammary gland lobules.
-
Mammary Gland Lobules- There are fifteen to twenty irregularly shaped lobes in each breast. They contain alveolar glands and a duct that leads to the nipple.
-
Nipple- The exit for milk production, located near the tip of each breast.
-
Areola- Circular area of pigmented skin which surrounds each nipple.
-
Ovaries- Each female has two of these glands in the pelvic cavity. They produce estrogen as well as produce gametes that are fertilized to form embryos.
-
Uterus- Commonly known as the ‘womb’ is the hollow organ that is responsible for the development of the embryo and fetus during pregnancy.
-
Vulva- The external female genitalia including the labia, clitoris, and urethral and vaginal openings. These parts work together to support urination and sexual reproduction.
-
Fallopian tube- A pair of tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. The egg cells are carried to the uterus through these tubes during ovulation. If sperm are present, the egg will be fertilized here.
-
Vagina- An elastic muscular tube that connects the uterus to the vulva and the outside.
-
Urethra- This is a tube that carried urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
-
Urinary Bladder-A hollow organ that functions as the body’s urine storage unit. Urine comes from the kidneys through the ureters and leaves through the urethra.
(Taylor, n.d.)